Next Generation Data Center
As companies have grown more and more dependent on technology and data to connect with and serve their customers, demand on IT has skyrocketed. Technology organizations have responded to rising client demands and showcased huge innovations and solutions to cater to customer needs and challenges. With the growth of technology solutions and increasing reliance on technology, the need for next-generation data centers has also grown. ISG believes roughly 2% to 3% of the world's energy utilization comes from data centers alone, and that this number will only grow with the increased reliance on technology and data.
Of course, data centers today are no longer constrained by brick walls. Let’s take cloud as an example. Cloud should be thought as an overlay service with a physical data center underlay that resides somewhere or might even be spread across the globe. This means the interpretation of what constitutes a data center is evolving rapidly and can now be seen as a dynamic collection of cloud and traditional server resources that reside in disparate physical locations and have a smart service wrapper that brings them together. This is where the next-generation data center begins.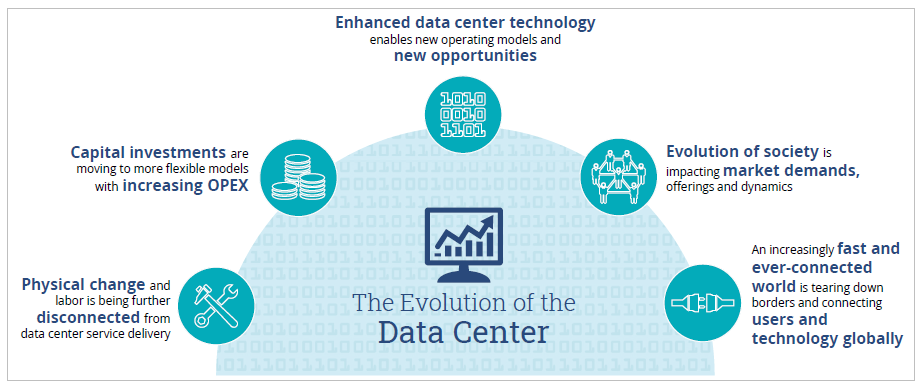
Figure 1: The Evolution of the Data Center
Challenges Facing Traditional Data Center
In a holistic sense, data centers face a number of issues. These include:
High cost of maintenance and management with major focus on fixed costs
High cost of energy consumption (and increase of tariffs)
High dependency on local human labor
Latency issues giving rise to relatively poor client experience
High initial capital investment with long depreciation periods
Slow pace of and limited potential for scalability
How is the next-generation data center solving these important issues? One of the biggest challenges with the traditional data center is the pain of managing a large infrastructure estate with high dependency on human involvement. Historically, management of IT infrastructure has been a tedious and labor-intensive manual process, which caused errors and inefficiencies that then required even more human intervention. Labor and estate costs could not be easily adapted to volatile demand or business development needs and incurred a consistently high expense.
This ISG white paper Evolution of the Data Center: How to Modernize Your IT Infrastructure explores how data centers are changing to support the enterprise of the future.
