It is a well-known fact that increased adoption of data-generating devices, such as internet of things (IoT), wearables, sensors and connected devices, has led to the creation of massive data repositories across industries and business segments. Evolving from preventive to predictive maintenance, increasing worker safety and improving patient care are among the many beneficial use cases driving the adoption of this technology. All these use cases have a common need – speedier analysis and swift implementation of insights from the data generated. This has triggered the need for real-time analytics, which leverages data from related systems for analysis as soon as it is recorded in the database. To achieve this, enterprises must consider a data management strategy that addresses integration of data at an enterprise level across systems. It is imperative for any enterprise, now and in times to come, to include data integration in their IT systems.
In-memory databases provide the infrastructure for this kind of data analysis across integrated systems. These databases permit data analysis and data recording simultaneously. SAP HANA, which is SAP’s in-memory database platform, provides a solution for enterprises seeking integrated data management and analysis across IT systems, when SAP is an anchor enterprise application. SAP HANA eliminates the scale barrier for analysis of complex data sets and allows real-time business insights. The HANA platform can assess data gathered from business applications across SAP solutions, third-party solutions and custom applications, thus enabling real-time analytics across systems in an organization.
Implementing In-memory Databases — Considerations for Enterprises
Enterprises should consider architecting their IT infrastructure to enable data collation from different sources and data storage in in-memory databases. The infrastructure should enable collation of data from different sources (including sensors, smart devices) through gateway technologies across devices, using increased network bandwidth and storage servers. The data collected from disparate data streams need to be correlated to enable analysis and management of different types of data. The following illustration shows a high-level view of the components involved in a real-time analytics system.
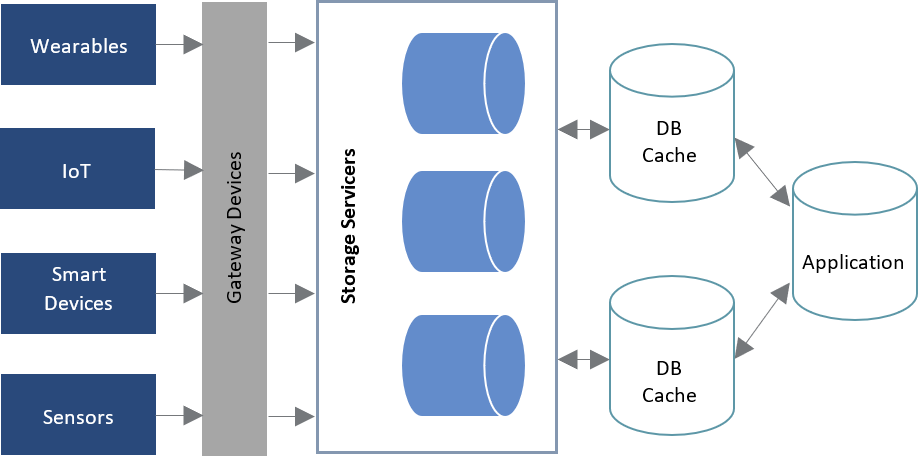
Figure 1: Typical Environment for Real-time Analytics
These components also should enable interoperability for an in-memory database to work at its fullest potential. The components should provide system interfaces to exchange data from different sources or different IT systems. This permits processing of complex data sets across integrated systems, thereby allowing data governance, data integration, data scalability and the ability to enhance analytical capabilities.
Current Adoption and Scope for Advanced Functionalities
Real-time analytics enables enterprises to implement changes across their business functions and realize return on investment (ROI) while improving processes, implementing new products/services or enabling better customer experience. Companies are leveraging analytics for real-time monitoring, decision-making, hyper-personalization of customer services and fraud detection. Companies in manufacturing, retail, consumer packaged goods, banking and financial services have seen increased adoption of real-time analytics and machine learning across various scenarios.
Many organizations that are building an intelligent enterprise – an amalgamation of intelligent processes, products and capabilities enabled by technologies such as machine learning, artificial intelligence and blockchain – use SAP HANA systems. Implementing real-time analytics is the first step toward establishing an intelligent enterprise. The HANA platform allows integration with other solutions or with SAP Leonardo, which encompasses IoT, artificial intelligence and blockchain on the SAP Cloud platform. These capabilities allow enterprises to implement innovative solutions, such as linking an in-store mobility system to customer data to improve customer response time at retail outlets, automating inventory replenishment and predicting new growth areas. All these current and future scenarios help in building businesses for next-gen enterprises.
Service Providers Are Enabling Digital Transformation by Using SAP HANA
Most service providers are providing SAP HANA solutions to enterprises as a proposition to transform their businesses digitally. In addition to integration or deployment of these solutions, providers are offering transformation roadmaps and post-deployment services to their clients. Since SAP HANA provides data management and analytics-based intelligence capabilities, the solution helps create an operational framework and expand business processes. Service providers are providing innovative solutions to improve data access and support advanced business insights, which contribute to real-time analysis and faster decision-making. Some of the service providers are leveraging bots for automating tasks and responses, thereby reducing the time required for issue resolutions across managed services.
The ISG Provider Lens™ Quadrant research study on SAP HANA and Leonardo Systems assesses service providers’ capabilities on SAP’s S/4HANA, BW/4HANA and Leonardo solutions across the global, U.S., U.K., Nordics, Brazil and German regions.
